In this session of CCNA tutorials, we will be going to discuss the characteristics of Cisco network topology architecture. This topic contains an overview of Network topology architecture, the difference between network topology and network architecture, different network topology architecture used in Cisco data centers and large business networks.
Overview of Network Topology Architecture
Network topology architecture defines the complete overview of any organization’s network infrastructure. Generally, network topology and network architecture are different terms often confused by many that their meaning is the same. Let me explain in brief that how do they define separately.
Network topology is the arrangement of network components using the network media. The arrangement can be physical or logical. In other words, the devices are connected with each other by means of network media. There are different types of network topology defined in networking theory such as bus topology, star topology, mesh topology, ring topology and so on.
You can click on the link below to know more about network topology in detail:
Whereas, network architecture defines the overall design of the computer network. It is the complete framework of the network that defines the logical and the structural layout of the network systems and their associated hardware such as routers, switches, endpoints and the network media.
The network architecture is of two types: peer to peer and client-server. You can click on the link below to know more about the network architecture in detail.
Different Types of Network Topology Architecture
The different types of network topology architecture incorporated by Cisco for their complex network afre
- 3 tier architecture
- 2 tier architecture
- Spine leaf Architecture
- WAN Architecture
- SOHO
- On-premises and Cloud
3 tier Architecture
Three-tier architecture is designed for large enterprise networks. It is also called a three-layered hierarchical model. The three-tier model consists of three layers.
- Access Layer
- Distribution Layer
- Core Layer
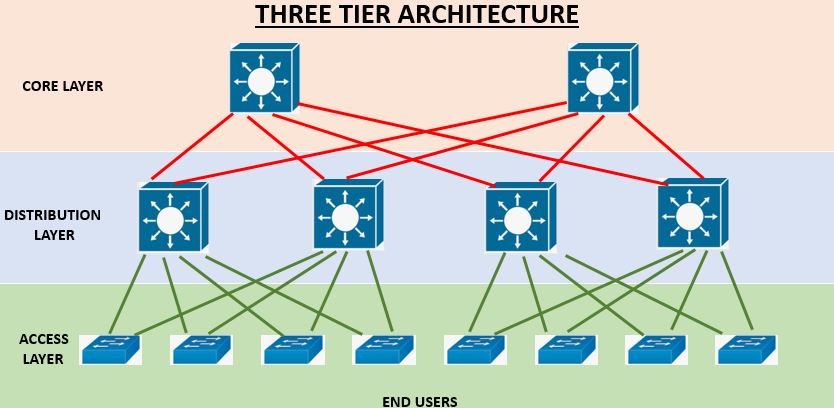
Access Layer
- It is the first layer of a three-tier architecture.
- It allows network access to the end-users and the end devices.
- It incorporates layer 2 network access switches that provide connectivity between the workstations and servers.
- It acts as the first line of defence in network security.
Distribution Layer
- This is the middle layer that lies between the access and the core layer of three tier architecture.
- It is also called the aggregation layer because it acts as an aggregation point for all the access layer switches.
- The distribution layer incorporates multilayer switches.
- It acts as the boundary between the layer 2 access domain and the layer 3 routed network.
Core Layer
- This is the layer of the three-tier architecture.
- It is the backbone of the complex network architecture.
- It incorporates high-speed network devices like Cisco Catalyst switches.
- The core layer aggregates the traffic from all the distribution layer devices and provides fastest switching and routing among multiple network components.
- The core layer devices are designed to be highly available and provide non-stop services with always-on mode.
- The core layer is designed to provide a high degree of redundancy with disaster recovery provision.
|
Note : Switching is performed between the access and the distribution layer. Routing is performed between the distribution and the core layer. |
Two-Tier Architecture
In two-tier architecture, the distribution and the core layer are collapsed to form a single layer. The new collapsed layer is named as collapsed core layer.
Spine and Leaf Architecture
- The spine and leaf architecture is a two-layer architecture consisting of leaf switches and spine switches. The spine and leaf architecture is mostly used in modern data centre networking infrastructure.
- Lots of things have changed over the years in network topology architecture. The traditional three-tier architecture has certain drawbacks and limitations. It is no longer used in modern data centres.
- The three-layered architecture is based on South the north flow of data traffic. The major drawback of the South to North flow of traffic is the increased latency period because traffic has to pass through network devices of all three layers.
- The spine and leaf architecture is based east-west flow of traffic. The need for modern data centres like low latency and high-speed switching and routing is fulfilled by the spine and leaf architecture.
- The spine-leaf architecture is composed of the leaf layer and spine layer.
- The leaf layer consists of access switches (leaf switches) to connect the end devices (servers and workstations) with the backbone network. The access switch is also called the TOR switch (Top of the Rack) or EOR (End of the Rack) switch.
- The spine layer is the backbone of the spine-leaf architecture and interconnects all the leaf switches.
- In the spine-leaf network model, every leaf switch is connected to the spine switch in a full-mesh topology.
- The latency issue and bottleneck problem of the three-layered network are resolved by the sone leaf architecture at a predictable level.
- The traffic has to hop spine switch and back to leaf switch.
- The other advantages are scalability, redundancy and more flexibility.
WAN (Wide Area Network)
WAN is a large network that spans a greater geographical area and is composed of two or more LANs or other networks.
WAN can be private or public. The private WAN can be the private network of an organization or the business owners that are connected with different LANs located at different locations. The two geographically isolated LANs at different locations are connected through leased lines or MPLS (Multi-Protocol Label Switching) hired from ISP or service provider.
The public WAN is the internet.
The WAN uses different topologies. The most common topologies are
- Point to point topology
- Hub and spoke topology
- Full Mesh topology
- Dual home topology
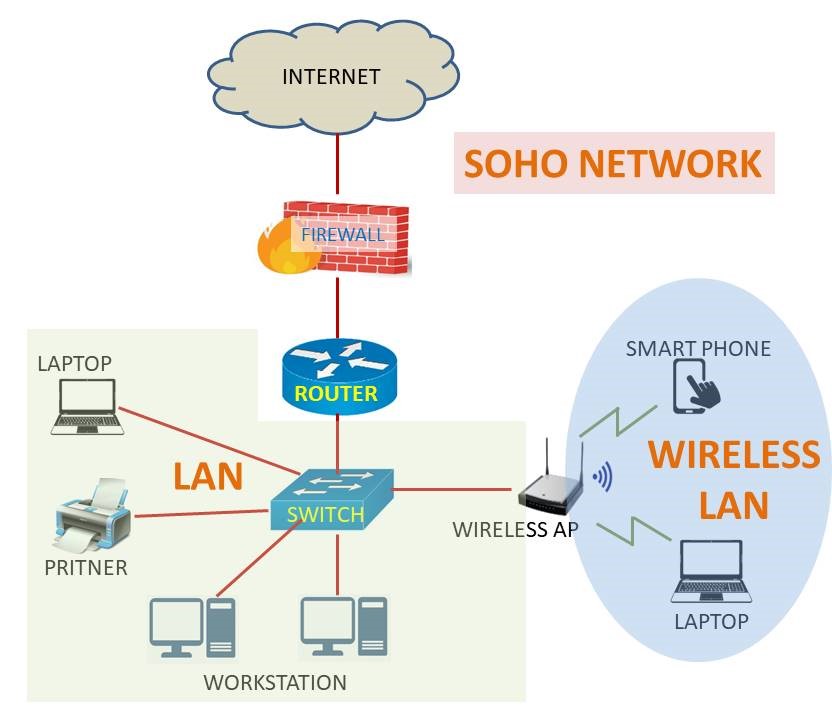
SOHO
SOHO stands for Small Office / Home Office Network. Nowadays most entrepreneurs and small business owners prefer to work from home. Else, they establish a small office space with limited networking devices to run their business smoothly. Most of these SOHO networks are connected to the internet and cloud and provide access to their clients and employees using the internet using minimum resources.
To establish a SOHO network whether, at home or a small office, you need an internet connection, a router, one or two network ethernet switches, access points, PC or laptops. Atypical SOHO network architecture looks like as under:
On-premises and Cloud
In today’s scenario of rapidly changing infrastructure, cloud computing, or simply cloud has become the most trending term and many IT companies and organizations are migrating towards cloud solutions for their business growth. There are still some organizations that still rely on on-premise services.
From the CCNA perspective, I will explain the brief introduction of cloud and on-premise service. Let us understand these two terms separately.
What is On-premise?
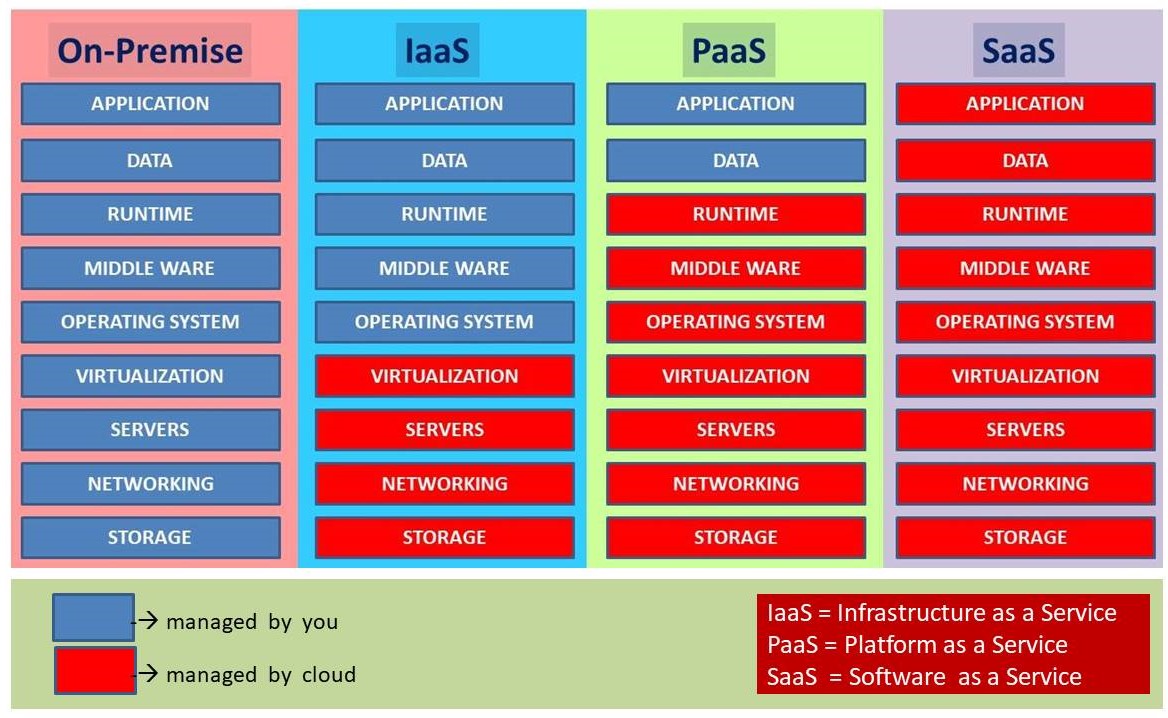
On-premise is the in-house set-up of the IT infrastructure of a company or an organization. Servers and other network resources are available to its client locally within the organization.
On-premise is a traditional approach to providing computing services to the client within the organization. The network resources such as servers, data storage, application and database are the sole property of an organization. It is managed and administered by the company itself.
What is Cloud?
Cloud computing or simply cloud is the online and on-demand computing services over the internet. The customer can avail of cloud service as per pay for use basis. The cloud service is easily accessible from anywhere, anytime and from any device.
Most IT companies migrate to the cloud service because of its low infrastructure cost. The company don’t need to install costly high-end data centres and IT infrastructure to make its business run smoothly. The cloud service provides almost all the network resources whether it be hardware or software.
The cloud service is broadly divided into three categories.
- SaaS
- Paas
- IaaS
SaaS
SaaS stands for Software as a Service. SaaS is a form of cloud service where applications are hosted in cloud servers. Users are allowed to access the application using the internet and web browser. No additional software or applications are required to install at the user end. The user can access the cloud application through a web browser.
The application service is provided to the user as per the demand of the user. Hence, SaaS is also termed as On-demand software. Examples of SaaS are Office 365, Cisco Webex, etc.
PaaS
Paas stands for Platform as a Service. Paas is a type of cloud service that provides a computing platform for software developers to test, run and develop software programs. It provides run time runtime environment for the programmers to compile and debug programming code using cloud service. The programmers don’t need to install different compilers and code editors at their local machine.
Examples of Paas are AWS Elastic Beanstalk, Windows Azure, Google App Engine etc.
IaaS
IaaS stands for Infrastructure as a Service. IaaS is also referred to as Hardware as a service. It is another type of cloud service that provides computing infrastructure managed over the internet. IaaS provides IT infrastructure resources such as physical and virtual machines, virtual storage space, virtual machines, VLANs, and other software bundles using software virtualization.
IaaS is a highly scalable service and provides GUI and API bases access to the client.
Examples of IaaS are Microsoft Azure, Amazon AWS, Google Compute Engine
Comparison between On-Premise, IaaS, PaaS and SaaS
| ←Prev | Next→ | |
| Endpoints and Servers | Physical Interfaces & Cabling Types |






