In this section of CCNA 200-301 exam tutorials, we will discuss how to configure and verify EtherChannel (LACP). EtherChannel is a technology that allows multiple physical links between two devices, such as switches or routers, to be treated as a single logical link. This enhances network performance and availability by increasing bandwidth, balancing traffic across multiple links, and providing redundant links in case of a link failure.
EtherChannel works by grouping multiple physical links together and configuring them as a single logical link using a common protocol such as Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP) or Cisco’s proprietary Port Aggregation Protocol (PAgP). Once the links are grouped together, they behave as a single link with a aggregated bandwidth and a single link-state.
EtherChannel provides several benefits to the network, including increased bandwidth capacity, load balancing of traffic across multiple links, and improved reliability through the use of redundant links. It is commonly used in high-performance environments such as data centers and enterprise networks.
Features of EtherChannel are as follows:
1. Increased Bandwidth: EtherChannel combines multiple physical links into a single logical link, increasing the available bandwidth. The physical links may be of different types and speeds, and they can be connected between switches, routers, and servers.
2. Load Balancing: EtherChannel distributes traffic across the physical links based on a load-balancing algorithm. This ensures that the traffic is evenly distributed across all available links, which prevents congestion on any particular link.
3. Redundancy: EtherChannel provides redundancy by allowing the logical link to continue functioning even if one or more of the physical links fail. This helps to increase network uptime and availability.
4. Simplified Management: EtherChannel simplifies the management of network infrastructure by reducing the number of physical links that need to be managed. This reduces administrative overhead and helps to ensure consistency in network configurations.
5 Spanning Tree Protocol Optimization: EtherChannel provides Spanning Tree Protocol optimization by reducing the number of Spanning Tree Protocol instances required. This improves network convergence time and reduces network complexity.
EtherChannel Protocols
The EtherChannel protocol uses several different algorithms to determine how traffic is distributed across the multiple links in the bundle. These algorithms include:
Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP)
LACP enables switches to dynamically negotiate the creation of an EtherChannel and exchange configuration information. It is an open source protocol and supports multi vendor environment.
LACP works in three modes.
On – In this mode, there is no exchange of LACP packets.
Active – In this mode, interfaces negotialtes with each other by exchanging LACP packets.
Passive – In this mode. intertface resond to LACP packets , but cannot negotiate with ther interface.
When various modes of LACP are enabled in two switches, the following results of Etherchannel formation are noticed.
| Switch 1 mode | Switch 2 mode | Etherchannel formation |
| ON | ON | Yes |
| ON | ACTIVE or PASSIVE | NO |
| ACTIVE | ACTIVE or PASSIVE | YES |
| PASSIVE | ACTIVE | YES |
| PASSIVE | PASSIVE | NO |
Port Aggregation Protocol (PAgP)
PAgp is Cisco propriatery protocol . It runs exclusively on Cisco device only. It has also three modes.
On – In this mode, there is no exchange of PAgP packets.
Desirable – In this mode, interfaces negotiates with each other by exchanging PAgP packets.
Auto – In this mode. interface resond to PAgP packets , but cannot negotiate with other interface.
When various modes of PAgP are enabled in two switches, the following results of Etherchannel formation are noticed.
| Switch 1 mode | Switch 2 mode | Etherchannel formation |
| ON | ON | Yes |
| ON | DESIRABLE/AUTO | NO |
| DESIRABLE | DESIRABLE/AUTO | YES |
| AUTO | DESIRABLE | YES |
| AUTO | AUTO | NO |
Static EtherChannel
This protocol manually defines which ports are part of the EtherChannel and how traffic is distributed across them.
How to Configure EtherChannel
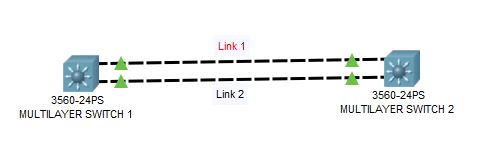
Let us take an example of above topology using two multilayer switches and will explain how to configure Etherchannel using two physical links. Here, two multi layer switches Switch 1 and Switch 2 are connected with two GigabitEthernet ports 0/1 and 0/2.
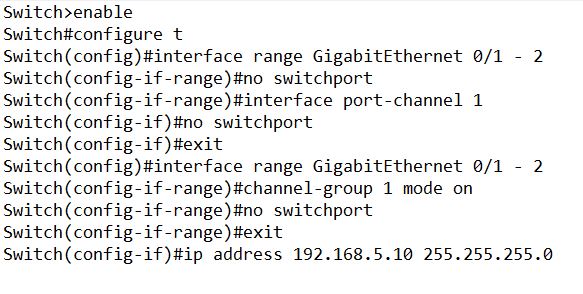
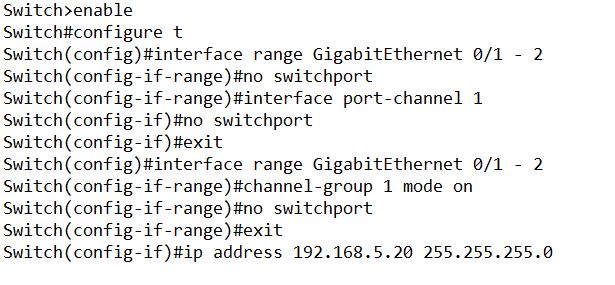
IP addresses for Switch 1 and Switch 2 are 192.168.5.10/24 and 192.168.5.20/24 respectively.
Step 1: Configuration of EtherChannel in Switch 1 is as under.
Step 2: Configuration of EtherChannel in Switch 2 is as under.
How to Verify EtherChannel
The following command is used to verify Etherchannel in Switch 1
| Switch#show etherchannel summary |

| ← Prev | Next → | |
| Configure and Verify Layer 2 Discovery Protocol (CDP & LLDP) | Introduction to Spanning Tree Protocol |